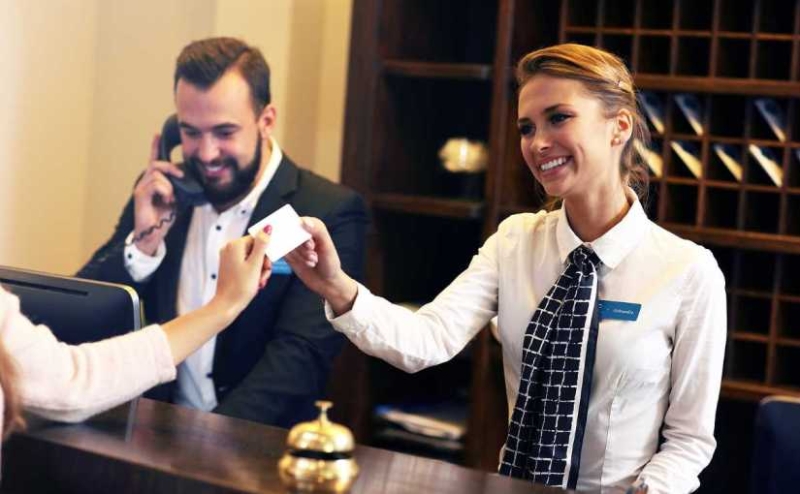
On November 4, 2024, New York City Mayor Eric Adams signed legislation to ensure hotel safety that will mandate a comprehensive licensing system for hotels to operate in New York City, implement several consumer safety protections, and require hotels to maintain continuous front-desk coverage, directly employ certain “core” employees, and provide human trafficking recognition training.
Quick Hits
New York City enacted a new hotel safety law that will require hotels to obtain a license to operate in the city and impose certain staffing requirements.
The law will require hotels to directly employ core employees, mainly housekeepers and front desk staff, avoiding the use of third-party staffing agencies.
The law is set to take effect 180 days after signing, or May 3, 2025.
The Safe Hotels Act, Int. No. 0991-2024, represents a significant shift in the regulatory landscape for New York City hotel operators, imposing several new employment and consumer compliance requirements as the city’s tourism industry rebounds from the pandemic.
“Our top priority from day one has been to keep people safe, and that includes protecting workers and tourists at our city’s hotels,” Mayor Adams said in a statement announcing the signing of the law. “That’s why we are expanding protections for the working-class New Yorkers who run our hotels and the guests who use them.”
Here is a breakdown of the key aspects of the new law.
Licensing
Under the new law, all hotel operators must obtain a license to operate within New York City. The license, valid for two years, requires a fee of $350. Hotel operators must submit detailed applications demonstrating their compliance with various staffing, safety, and operational standards. Violations of the new licensing requirements can result in significant civil penalties, ranging from $500 for a first offense to $5,000 for repeated offenses.
Staffing
The law will require hotel operators to provide continuous front desk coverage, either through front desk staff or, during overnight shifts, a security guard trained in human trafficking recognition. Large hotels (those with more than 400 rooms) must also maintain continuous security guard coverage on the premises.
Further, the law will require large hotels to directly employ certain “core employees,” aiming to eliminate the use of third-party contractors for core staffing needs. The law defines “core employees” as “any employee whose job classification is related to housekeeping, front desk, or front service at a hotel.” The law exempts small hotels, defined as those with fewer than 100 rooms.
The law will also prohibit hotel operators from retaliating against employees who report violations, participate in investigations, or refuse to engage in practices they believe to be illegal or unsafe.
Consumer Protections
Hotels will be required to maintain the cleanliness of guest rooms and common areas. Daily cleaning and trash removal are mandatory unless explicitly declined by the guest. Hotels will not be allowed to charge fees for daily room cleaning or offer incentives to guests to forgo this service.
Safety
The law will require hotels to provide panic buttons to employees whose duties involve entering occupied guest rooms. Additionally, all core employees must receive human trafficking recognition training within sixty days of employment.
Key Takeaways
Hotel operators may want to consider reviewing and updating policies to align with the new requirements, including updating staff training programs, security protocols, and cleaning schedules. They may also want to assess their staffing arrangements to ensure that core employees are directly employed.
The law is set to take effect 180 days after signing, or May 3, 2025.
© 2024, Ogletree, Deakins, Nash, Smoak & Stewart, P.C., All Rights Reserved.
by: Simone R.D. Francis , Zachary V. Zagger of Ogletree, Deakins, Nash, Smoak & Stewart, P.C.